Arsalan Syan: The Refugee Experience
Interview with Arsalan
Arsalan agreed to do this interview after I reached out to Church World Service, asking if they had anyone who had immigrated to Harrisonburg who would be interested in participating. Arsalan hoped that by sharing his story he could help people gain a greater understanding of the refugee experience in America, and help foster more compassion and understanding towards them. As a case worker with a refugee resettlement agency, and as a refugee himself, Arsalan is familiar with a wide range of issues that impact refugees to the United States and is thus an extremely useful resource for modern immigration patterns and experiences.
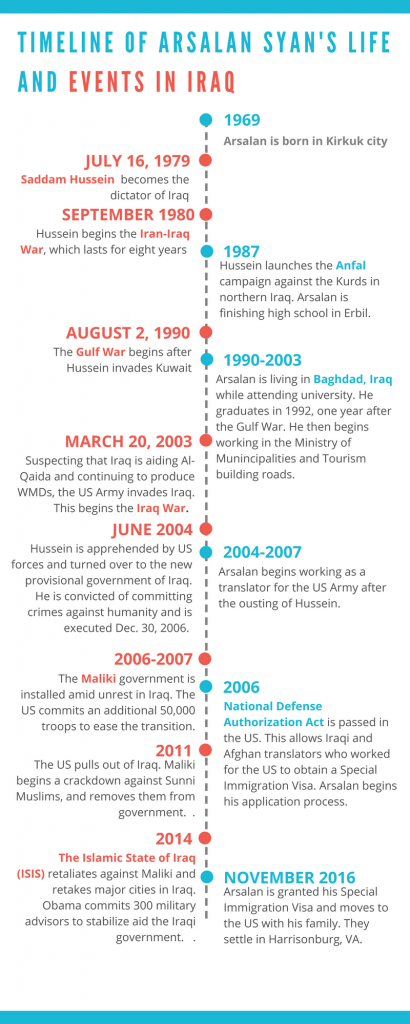
Going into the interview, I must confess I did not know that much about Iraq, or even the Kurds. As such, when I conducted the interview I didn’t ask as many questions about Iraq that may have been useful for future historians. The purpose of this piece is to help anyone using this interview as a resource to understand the historical context that Arsalan grew up in, and to help them understand what led to some of the immigration policies he’s personally dealt with. Below is a timeline of Arsalan’s life alongside one of major events in Iraq, which are explained in more detail below.
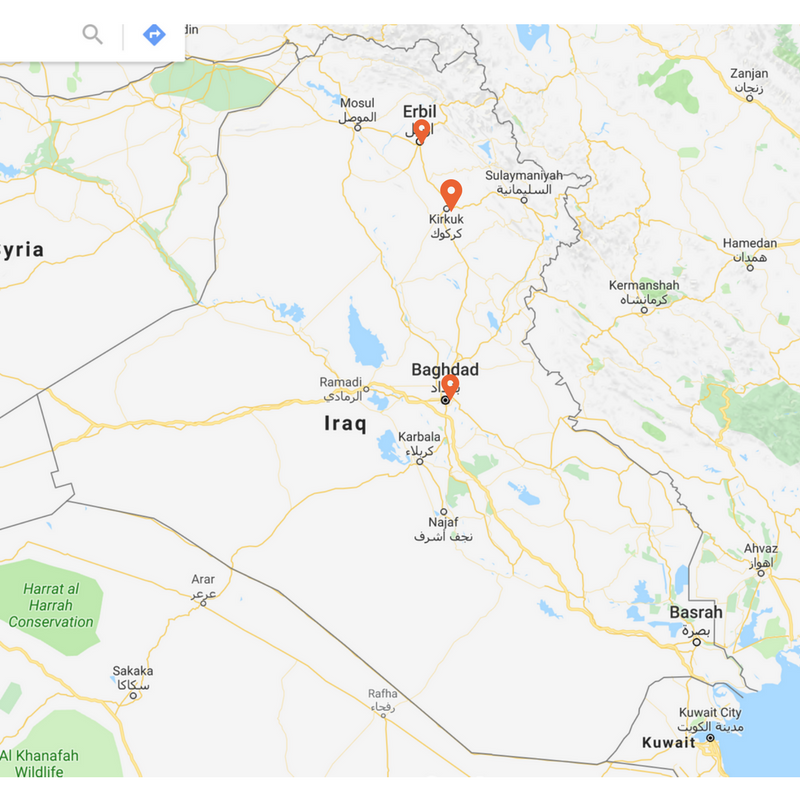
To help orientate the reader to the cities discussed in this piece, I have made the below map which marks where the cities of Kirkuk, Erbil and Baghdad are.
Early Life in Iraq:
Arsalan was born into a Kurdish family in Kirkuk city, Iraq in 1969. The Kurds are a stateless ethnic group that form minorities in Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran.[1] They have faced persecution in Iraq, and have tried for decades to assert their independence and establish the country of Kurdistan (the land of the Kurds). This desire for independence, much to the chagrin of the Iraqi government, has over the last few decades led to several violent confrontations between Kurdish nationalists and the Iraqi government in the northern part of the country.
Arsalan was born a year after the Ba’thist party, which had carried out a campaign of “Arabization” in the mid- 1960s that had displaced several thousand Kurds, had taken control of the Iraqi government. In order to preserve their fragile hold on the government, he party had negotiated a ceasefire with the Kurds in 1970, and had recognized the rights of Kurds in an interim constitution that year. It was a short-lived peace though, and hostilities between the two resumed in 1975. During this war, 600,000 Kurds were displaced and sent to collective settlements, while over 1400 Kurdish villages were obliterated. In Kirkuk, the Kurdish population was reduced and replaced by Arabs.[2] During my interview with Arsalan, he mentioned that he did not grow up in the city he was born in (Kirkuk), but instead spent his childhood in the city of Erbil, which is further north.
Arsalan was ten years old when Suddam Hussein became president of Iraq, assuming the role after his cousin, Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, had stepped down. Facing threats to his power from Shiite Muslims in Iraq, the Kurds in the north, and from Iran, Hussein started the disastrous Iran-Iraq War in September of 1980 in order to curb Iranian influence in the region.
Young Adult Life in Iraq:
During the war, Iran supported the Kurdish resistance in northern Iraq, which prompted retaliation from Hussein in the form of the Anfal (Spoils) campaign against Iraqi Kurds in 1987.[3] The campaign involved the destruction of hundreds of Kurdish villages, with the use of chemical weapons in many villages, and the clearing of Kurdish civilians to holding facilities.[4] Human rights investigators estimated that between 50,000 and 100,000 Kurds were killed during this campaign.[5] The violence only stopped after eight years of fighting between Iran and Iraq. After fighting each other to a stalemate, the United Nations brokered a ceasefire on August 20th, 1988, and Iraq was left economically drained, and in debt.
Possibly to counteract some of the economic difficulties that Iraq faced, on the 2nd of August 1990 Hussein invaded Kuwait. Arsalan had recently begun his studies in engineering at the University of Baghdad when this conflict began. The international community condemned the invasion and called for Hussein to withdraw. When he refused, a US-led coalition began an areal bombardment campaign against Iraq, which started the Gulf War (17 January-28 February 1991).[6]
Along with the bombing of Iraq, the coalition also cut power and water lines to the capital city of Baghdad which made conditions in the city so horrible that Hussein risked an uprising. As a final effort to draw the coalition into a ground war, where Iraqi forces could hopefully beat them, Hussein set the Kuwait oil fields on fire on February 22, 1991.[7] This proved disastrous, as the Iraqi forces were crushed by the coalition who drove back the Iraqi forces on the 25th of February 1991. Iraq was forced to surrender, and on the 28th of February, UN resolution 687 laid out the terms for a ceasefire and placed restrictions on the Iraqi government. Under this resolution, Iraq was required to destroy all their weapons of mass destruction (WMDs), and submit to UN investigations to show their compliance.[8]
There was relative peace in Baghdad for a time after the war, and Arsalan was able to graduate in 1992 with his degree in engineering. Soon after he began working as the head of the mechanical department in the Ministry of Municipalities and Tourism in Baghdad, helping to rebuild the infrastructure of Iraq. In 1993 he married his wife, Sakar Mahmood, and began to raise his family. While living in Baghdad the couple had four sons: Sivar, Danar, Renar, and Ali.
The Iraq War- Arsalan begins work as a translator:
It wasn’t long before war came to the country again, however. In the wake of 9/11, United States President George W. Bush claimed that Iraq was continuing to produce WMDs, and that they were aiding the terrorist organization Al-Qaida. Against the advice of the international community, Bush issued an ultimatum to Hussein on March 17, 2003: Leave Iraq willingly in 48 hours or be removed by the US military.[9] Hussein did not comply, and on March 20th the United States military invaded.
The force swept rapidly through the country, taking the capital city of Baghdad on April 9th. By December 13, the US had apprehended Saddam Hussein, turning him over to the Iraqi forces in June 2004. He was convicted of committing crimes against humanity and was publically executed on December 30, 2006.
Following the deposition of Hussein, the Bush administration approached Nouri Kamilal Maliki, a Shiite politician, and convinced him to run for prime minister. As a political unknown, the Bush administration felt that he would help to curb the growing sectarianism between the Sunni and the Shiite.[10]Maliki was successfully elected as prime minister in May of 2006, and helped ease the conflicts between the Sunnis and Shiites, along with several other key factors. One factor that helped bring more stability to Iraq was the “Surge”. In response to the growing unrest in the country, and to help the country transition into democracy, President Bush committed another 50,000 troops to Iraq in January of 2007.[11]It was during this time that Arsalan began working as a translator for the US military based in Baghdad.

Lunch with Military Personnel and Families with the Prime Minister of Iraq. Photo credit: The White House Archives
The Bush administration and Pentagon officials hoped to keep US forces in Iraq past 2011, as the country was still in a fragile state and Maliki was beginning to show sectarian tendencies that concerned them. However, when Barack Obama was elected to the Presidency in 2008, the withdrawal of US forces from Iraq was one of his priorities. In 2009, Obama officially announced that all US troops would be recalled from Iraq by the end of 2011.[12]
With the Obama administration’s gradual withdrawal of troops, and without the Bush administration keeping restraint, Maliki began to consolidate his power and displayed strong bias in favor of Shiites. These actions deeply concerned officials at the Pentagon, who strongly urged Obama to keep a residual force in Iraq. Obama did not, and in the spring of 2011 the United States military fully disengaged from Iraq.[13]
The Rise of ISIS and Migration to the US:
With all restraints gone, Maliki began a violent crackdown against Sunni Muslims in the government and military. This sparked outrage from Sunni Iraqis, and led them to enlist the support of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISIS) and former Ba’thists in 2014. Together, this combined force took Fallujah, Mosul, and Ramadi. Maliki revived the Mahdi army to try and combat this force, but was crushed by the opposition. Obama was forced to order 300 military advisors back to Iraq to deal with these developments.[14]
As the war against ISIS continued, Arsalan was finally granted his Special Immigration Visa (SIV) thanks to a program established by the Bush administration through the National Defense Authorization Act of 2006. This act authorized the issuance of fifty Special Immigration Visas to Iraqis or Afghanis who had served as interpreters for the US forces, and who met certain requirements. The Bush administration recognized the dangerous risk that many translators like Arsalan took in aiding the US forces, as they became targets of extremists who accused them of aiding the US occupation, and so established this program to provide them an avenue to the US. Under this act, any Iraqi or Afghani translator who had worked for the US forces at either the Baghdad or Kabul embassies for at least a year could apply for an SIV.[15] When this program was made known to Arsalan in 2007, he reached out to the US ambassador at Baghdad to see how he could apply for one.
Arsalan was one of the lucky few able to obtain one of these visas, although it took him nearly ten years to receive it. In November 2016, he and his family boarded a plane for Washington, DC, where they continued on to settle in Harrisonburg, Virginia. On this visa, he was treated as refugee, and the Church World Service refugee resettlement office helped him and his family settle into the US with a government stipend and with assistance in procuring a job.
Arsalan’s experience with the United States refugee program is typical of many. While the government assistance helps tremendously, he did mention that many refugees do not get enough assistance in learning the English language. In his view, this is one of the biggest hurdles for refugees, and can inhibit their ability to find work and get through the system. He was lucky, in that he was already familiar with English, but many others struggle immensely with it. Another issue with the refugee program is that it does not provide health insurance beyond the initial three months, which becomes an issue of great anxiety for refugees who otherwise cannot afford it.
Arsalan’s interview provides powerful insights into the experience of refugees in the United States, through his discussion about his work as a case worker at a refugee resettlement office. He is also a valuable source of information for events that occurred in Iraq and led to the establishment of the Special Immigration Visa Program. Future interviews could yield more useful information for historians.
[1] “The Time of the Kurds,” Council on Foreign Relations, October 4, 2017, accessed April 14, 2018, https://www.cfr.org/interactives/time-kurds?gclid=CjwKCAjw2dvWBRBvEiwADllhn-lWPGdaz2vF0hY3osX_NT-J-AplWTIRn_0LAOgnfUdqU0VT3-Z34BoC2FIQAvD_BwE#!/time-kurds?gclid=CjwKCAjw2dvWBRBvEiwADllhn-lWPGdaz2vF0hY3osX_NT-J-AplWTIRn_0LAOgnfUdqU0VT3-Z34BoC2FIQAvD_BwE.
[2] Phebe Marr, The Modern History of Iraq (Westview Press:2012) 233-237.
[3] Phebe Marr, 298.
[4] Martin Van Bruinessen, “The Kurds Between Iraq and Iran,” MERIP Middle East Report, no. 141 (1986), 14.
[5] Phebe Marr, 300.
[6] Daniel Beers, PhD, “The New Humanitarianism: “New” Wars of the 1990s,” (lecture, James Madison University, Harrisonburg, VA, March 15, 2018).
[7] Phebe Marr, 334-335.
[8] Daniel Beers, PhD, “The New Humanitarianism: “New” Wars of the 1990s,” (lecture, James Madison University, Harrisonburg, VA, March 15, 2018).
[9] The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica, “Iraq War,” Encyclopedia Britannica (Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc.: December 6, 2017) Accessed April 15, 2018, https://www.britannica.com/event/Iraq-War
[10] Losing Iraq (PBS:2014) Accessed April 16, 2018, https://fod.infobase.com/PortalPlaylists.aspx?wID=96579&xtid=114698.
[11] Phebe Marr, 451.
[12] Losing Iraq (PBS:2014) Accessed April 16, 2018, https://fod.infobase.com/PortalPlaylists.aspx?wID=96579&xtid=114698.
[13] Losing Iraq (PBS:2014) Accessed April 16, 2018, https://fod.infobase.com/PortalPlaylists.aspx?wID=96579&xtid=114698.
[14] Losing Iraq (PBS:2014) Accessed April 16, 2018, https://fod.infobase.com/PortalPlaylists.aspx?wID=96579&xtid=114698.
[15] U.S. Department of State- Bureau of Consular Affairs, “Special Immigration Visas (SIVs) for Iraqi and Afghan Translators/Interpreters,” U.S. Visas, accessed April 18, 2018, https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas/immigrate/siv-iraqi-afghan-translators-interpreters.html
For a more detailed history of Iraq and US immigration policy, view the research paper produced for this project, Historical context-Arsalan Syan
| Maria Matlock: | 00:01 | This is Maria matlock interviewing Arsalan Syan for the |
| immigration, uh, 439 immigration history course at Jmu. OK. So, | ||
| um, uh, when, and where were you born? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 00:19 | Kirkuk City in Iraq. A in nineteen- nineties, uh… 1969. |
| Maria Matlock: | 00:27 | And, um, did you grow up there or did you grow up somewhere |
| else? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 00:27 | Excuse me? |
| Maria Matlock: | 00:34 | Was that the, the place where you grew up, where you had you |
| spent your childhood or did you grow up in another place? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 00:39 | Yeah, I grew up in Erbil cities, a city around one hour distance |
| between my own city, and other city. Uh it’s called Erbil City. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 00:49 | OK. Um, and what was it like living there? What was it like living |
| there? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 00:56 | What was like, |
| Maria Matlock: | 00:58 | yeah, I’m like, what kind of experiences did you have living? Um, |
| in that place? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 01:04 | You mean my graduation and my experience or? |
| Maria Matlock: | 01:08 | Yeah, just like, um, what was your childhood? Um, like. Um, |
| what kinds of things did you do as a kid? Um you know where, | ||
| did you go in that city | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 01:18 | when? Uh, when I first six years I started the study and uh, uh, I |
| completed, uh, my engineering degree dsc engineering in | ||
| Baghdad city, that’s the capital of Iraq. It’s far from my city | ||
| around three, maybe five hours driving. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 01:18 | That’s a long drive. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 01:53 | I thought, “I will stay in Baghdad, not moving daily, so it’s just |
| stay there and | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 01:53 | [Arsalan’s wife comes in] Hi |
| Arsalan Syan: | 01:53 | I, uh, this is my wife, by the way. She’s named Sakar. |
| Sakar Mahmood: | 01:53 | Hi |
| Maria Matlock: | 01:53 | Hi, how are you? |
| Sakar Mahmood: | 01:53 | I’m nice, thank you. |
| Maria Matlock: | 01:53 | I’m Maria, it’s nice to meet you. |
| Sakar Mahmood: | 01:53 | Nice to meet you. |
| Maria Matlock: | 02:08 | Um, let’s see. Um, so what did you study when you were in |
| school? You mentioned engineering earlier. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 02:19 | Yes, I just uh, After I graduate high school, I joined with the |
| university that I studied, mechanical engineering, general | ||
| mechanical engineering. And I graduated at 1992. Then after | ||
| that I started working my job. So I work with the government, | ||
| uh as the head of the mechanical department, in the ministry of | ||
| municipalities and tourism, and I spent it the around 23 years, | ||
| but I moved to different places, like a different position higher | ||
| than that, What I started. But the last job that I, [coughs] Sorry. I | ||
| was a deputy of general director. The ministry after that, I | ||
| supervise at the 120 meter, as I mentioned to you before we | ||
| start, I think that’s the biggest road in urban city. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 03:30 | Right and how did you meet your wife? When did you get |
| married? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 03:30 | We married at 1993. |
| Maria Matlock: | 03:38 | And um, how did you meet her? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 03:40 | Actually, uh, uh, me and her cousin. Uh we was student in |
| university together and we have a far relation with this family. | ||
| But, I didn’t meet her before. I just meet with her cousin, and | ||
| we are students together. I feel that this family is a good family. | ||
| So I can find someone from this family that’s going to be my | ||
| wife for future. I ask him if, uh, they have a year, like a to | ||
| compare with my age is going to be OK with me. And he offered | ||
| to me, uh, his cousin, uh, because his wife, a sister with uh, my | ||
| wife, so he say that uh, uh, we have uh, my cousin and you | ||
| come speak her, and if you on if you feel that you can, Eh, | ||
| interesting together you kind of do the process. And I meet her | ||
| one time in the marriage ceremony. I feel that I am interested | ||
| with her. So we start the process. And we married. yeah. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 05:00 | And You said that you had four children earlier. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 05:00 | Yes. |
| Maria Matlock: | 05:04 | Um, how old are they and what are their names? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 05:10 | Uh the old one, His name’s Sivar. He’s 24 years now and he’s |
| working like a team leader in Shenandoah Grows. And the next | ||
| semester, on the summer semester he was starting his study in | ||
| a college community, that’s in Blue Ridge. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 05:10 | Ok. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 05:29 | Yeah in Bridgewater. And then my other son who’s named |
| Danar, he’s 22 years. He’s already student in the college, uh | ||
| Blue Ridge uh, what you call it? college. uh Besides his study, he | ||
| is working on the weekends in Marshall as a forklift driver. And | ||
| the other one, his name is Renar, he’s 16 years now. uh, Sixteen | ||
| years. Ah, he’s a great kid in high school. Harrisonburg high | ||
| school. And Ali, he is the small one, and he is uh only seven | ||
| years. And he is in Smithland elementary school, grade one. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 06:13 | All right. Um, so when did you leave Iraq? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 06:17 | I leave Iraq a actually, I arrived at United State on the twenty- |
| nineth, uh November 2016. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 06:28 | Ok, Um, so right in the middle of the presidential elections. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 06:30 | I have uh, uh, because we, we, uh, we have a special |
| immigration visa because after we arrived with united, because | ||
| after two weeks or maybe three weeks, we received our green | ||
| card. So we are permanent resident now. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 06:48 | Um, so what was it like coming in here during that time in |
| America? It was a very fraught political time. And especially with | ||
| um like the, the candidates that we had. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 06:48 | Um, I don’t understand your question, excuse me. |
| Maria Matlock: | 07:06 | Um, so what was it like seeing the elections going on here in the |
| us? like um seeing now President Trump and Clinton going | ||
| against each other in the election? um like, what were your | ||
| reactions to that? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 07:22 | Uh, I think that’s not the effected on us, because when we |
| arrived he had not started to be a president. After we arrived, | ||
| then he uh a president of the United States is a political |
decision, is sometimes is difficult for us as a refugee. But the, I believe he sometime speak something going to, uh, after that, uh, it’s something would be changed. So he, uh, maybe change
| his mind sometimes. I believe it’s a little confusing for us | ||
| sometimes, when he make a decision. And after that it’s going | ||
| to be clear, uh, the change of decision. In the beginning when | ||
| he, uh, when he, uh, president, he decided to get out all non- | ||
| United States resident to outside. But after that he changes that | ||
| plan to, for example, people who’s coming so big already on | ||
| there legally they can’t stay. But only the people who is not | ||
| coming, uh, like a closing border the yellow, they have much | ||
| anymore in the United Stated. And I don’t know if this is the | ||
| things that they use them sometimes for like people like us. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 08:57 | So what made you decide to leave Iraq? Why did you leave |
| Iraq? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 09:05 | Uh, we have, I forget to inform you that I worked at the, uh, |
| behind the United States army and I serve as the United States | ||
| army in our country, more than one year as a translator and | ||
| interpreter. Uh, so, uh, there is a law in united state, I believe is | ||
| that any county that the United States army to go to that | ||
| country and use the Army, and any people who leaving this | ||
| country help the United States army for more than one year | ||
| they have a right, and um their family, to get the visa and the | ||
| immigration process through to move to the United States after | ||
| the United State army leave that country. So after 2007 when | ||
| the United States Army is moving to outside, with the president | ||
| George w Bush when he make a decision the time, uh, after | ||
| that, uh, this immigration processes was open for people | ||
| whose, uh, was uh, working with the United States army, so I | ||
| just a send an email to the United States embassy in Baghdad | ||
| and I requested, for me and my family, our situation after the | ||
| United States Army moved. We are feeling, we are not safe in | ||
| this country anymore. So they make a decision and the forces | ||
| after that, we moved to the United States. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 10:44 | And um, did you come straight to Harrisonburg or were there |
| other areas that you stopped in? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 10:44 | No, straight directly to Harrisonburg. |
| Maria Matlock: | 10:44 | Ok. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 10:52 | And I mean the fly when we, uh, arrived to Washington dc, and |
| directly to, uh we not stay in Washington DC, we direct to | ||
| Harrisonburg. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 10:52 | What made you decide to come here? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 11:05 | I actually, we have no aid here before we come. Uh, which city |
| is better than the other in the United State? I, I just researched | ||
| something to find which city is more safe, more comfortable for | ||
| us. But the, actually we have some, uh, like a Kurdish | ||
| community here. In Harrisonburg.I hear that. And uh, we have a | ||
| relative, his name Uhmed, he was live here before we come and | ||
| he told me about this. This is area is fairly safe, and very good to | ||
| people who’s coming new. And jobs available, easier than other | ||
| places. Uh, uh, that’s why we decided to come to the city that | ||
| there’s some Kurdish people like a community with us. In the | ||
| beginning, you know, it’s not easy to go to the other country | ||
| and you not find in the city Anyone speaking your language is | ||
| going to be difficult. Uh, but, uh, anyway, uh, he was like, our | ||
| US tie with us and help us in the beginning, first month to find a | ||
| house, uh and Church World Service also provided services, | ||
| medical services for us. But he’s also helped with the two | ||
| biggest of our sons to the schools and health insurers. Um, uh, | ||
| that’s, it’s like a relative. It’s good. Better for us. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 11:05 | Um, so, um how did you start working at the CWS? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 12:55 | Um, actually when we arrived with the United States, the CWS |
| provided many, many things, uh, services for me and for my | ||
| family. Like you’re finding house for us, furnishing the house, |
provides food, help us to register for the food stamp in the beginning before you start to work, and they help us to find a job for me, for my sons, for my wife. In the beginning I worked in Ariake, because it’s, you know, when you arrived to other like United States you cannot find a job for. I have BSC degree in engineering, but I believe that’s not easy for you to find a job equivalent to my experience, so I decided to start any job available in the beginning to …to get some income for me and my family and I work at as a mechanical, uh mechanic operator in Ariake, but after two, three months I feel that this job is very hard to me because it was a night shift starting from 7:00 PM to 7:00 AM. All the night. It was very hard job. Then I, eh, feel that I’m not healthy and I visited a doctor. He told me, you cannot continue with this job so you have to move to other positions. After that…that this job actually not CWS find to me. Social services, because I applied for ten-up also. So they provided this offer to me, eh but I told them that I cannot do this job anymore. And they try to find some position, like a cargo marshall. I feel that this job also is maybe it’s not. Then I decided to find a job by myself. I searched through the internet, and try the civil cases. And then finally I find the job is filling a machine operator, a second shift in Andrews, uh, Andrews Food North of America. Uh, I feel that this position is OK me, especially working at a computerized, and you can by the
| computers control the machines and it’s easier and closer to my | ||
| experience. So I started seven month, eh, working there. And | ||
| they’re finally, Lucia, I think you know her, she’s a caseworkers | ||
| in CWS. She’s called me and she offered to me that there is a | ||
| position available that case worker for Polish, Arabic, and | ||
| English language. If I am interested in, I can go on and fill out | ||
| the form and apply for this position. Then I decided that this | ||
| position is OK with me, uh, and it’s office work, not that hard | ||
| like uh planned places. Uh, so I decided to go and fill out the | ||
| form, and eh make the interview. And then they decided that | ||
| I’m qualified for this position. And it was supposed to be a | ||
| temporary job for three months. After the, eh during this | ||
| agreement, if I prove it that I am qualified person for this | ||
| position, they make a decision to be available to employ for that | ||
| long time and staying with them. After two month, not three | ||
| month, they decided that I’m qualified for this position. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 12:55 | Oh, that’s great! |
| Arsalan Syan: | 16:56 | So they make the decision, eh yeah, that I’m staying be a regular |
| full-time employee with them as a case worker. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 17:00 | Ok, and what do you do as a case worker? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 17:04 | As a case-worker I am, um, working on the RMP, RMP |
| replacement and the replacement of placement. That’s a | ||
| position is there for the people who’s new coming on the first | ||
| three month we provide on… uh, before they come, we | ||
| know…we get a notification that, the capacity of the family, | ||
| how many, and if they have a disability or they have uh big kids | ||
| or small kids… daughter, son. We, we, we know everything | ||
| about this family. Uh, then we try to find the house for them. | ||
| We have some sources, like agencies help us as the CWS to find | ||
| the house, compare with the capacity of the family. And then, | ||
| for example, if they have a disability, we know not find an | ||
| apartment on the third floor, for example. We have to think | ||
| about all these issues, uh, uh, after we find the house or we do | ||
| a, like a, an inspection for the house to see if it’s healthy or not. | ||
| Uh that’s our responsibility. And after we make sure that the | ||
| house is ok, we make an agreement with uh, the uh, land | ||
| owner. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 18:22 | And then, uh, we furnish a simple furnishings that require to the |
| family, like a sofa, like a kitchen table. Uh, the kitchen should be | ||
| available with all the things that are like to open and you no, |
[coughs] excuse me, the simple requirement. It should be available like the eh hot water, cold water, electricity, a heating system, the AC system should be available in that house. And
| then we provide a depot one day, uh, before they come. Uh, | ||
| we, uh, we bring some foods are going to be like a, a normal | ||
| foods you’re using for one week or two weeks or keeping in the | ||
| house for the family. And in the day that they arrived, eh, we | ||
| have to go to the airport to escort him to the house. Sometimes | ||
| we not do that, we waiting an hour or… this because IOM | ||
| arrange these things with us, uh, for example, a renter to | ||
| provide the transportation for them to our office and we are | ||
| awaiting them on in our office, so when they arrived we just | ||
| introduced ourself as a CWS, and we are the case worker who’s | ||
| covering their cases. Then we pick up with the house and we | ||
| explain everything to him that said, for example, the open | ||
| house. How is the house working? Every details of the house, if | ||
| it’s um, if they arrived in the night we not take a long time with | ||
| them because, you know, we feel that they are very tired, | ||
| maybe because they have a long trip. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 20:15 | So we just give him some simple things. And then there we have |
| a next-day visit. The next day is very important and it’s required | ||
| for us as a case worker to make sure that everything is OK with | ||
| them. So the next day we’re going to visit him to see if they | ||
| need anything, that they are all healthy or they need some help | ||
| there, emergency things. Also that you signed the agreement | ||
| between the landlord and the newcomer. And also we, uh, uh, | ||
| be given to him some cash money in case they need it, that’s | ||
| also required. Per adult is 50 dollar, per child is 25 dollars. That’s | ||
| maybe simple things they need. And then, uh, within seven days | ||
| we have to arrange an appointment with him, let’s call it, uh, | ||
| orientation, uh, the family they are, we pick up into the office | ||
| and we have several people that’s working in different fields like | ||
| education, like a help, like a job, like a community. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 21:38 | So we meet together with this family on each one, provide the |
| service that he’s specialized in. For example, you have uh |
Megan, she’s specializing in the accounting issues. And Sara, she’s in education. If they have a… kids that need to go to register to the school Sara is going to help them. If they need a, for example, for Medicaid and other issues, uh, Megan, she’s responsibility. For the food stamp in the beginning because they have no job for the … because, uh, also they need, uh, uh, some, uh, like a help, like a food stamp. So a that’s my responsibility to fill out the form. And also we have to register the, and make an appointment with the social security administration to get them social security card. That’s my responsibility also. And uh, we have to enter another appointment with the social services. That’s one, the staff for snap and food stamp and if they need to apply for the tenant.
| Arsalan Syan: | 22:46 | So you have to arrange also another appointment. That’s all the |
| things that we have to do in the first week. Uh, we another | ||
| program, we call it the MIC. That’s for the parents who have a | ||
| kids say under five years, uh, we have to apply also for these | ||
| services. Also beside that, we have a match grant, that’s a | ||
| matching grant. That’s the other program. It’s also a CWS | ||
| provided to the family before they start the job. But it’s a little | ||
| like… a complicate. If he applied for tenant, he cannot apply for | ||
| the matching grant. If he apply for matching grant he cannot | ||
| apply for [tenant]. So we had to organize these thing eh with | ||
| that family. And uh, we explain everything to him to make him | ||
| understand that the, which one they, they decide to involve | ||
| with. Eh, also, I forget eh during the orientation, we do explain | ||
| everything to that family about the United States, about the job, | ||
| about how money is, how much is important the job in this | ||
| country to, people have to work and they have no disability | ||
| toward a up the. We have another visit, a family visit. It’s before | ||
| 30 days. I think I’m speaking a long time. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 24:18 | No, you’re fine. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 24:18 | It’s ok? |
| Maria Matlock: | 24:18 | Yeah, absolutely. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 24:21 | OK. Because I want to explain everything to you. |
| Maria Matlock: | 24:24 | No, that’s absolutely fine. It’s good to like here exactly, like, how |
| you’re helping these people getting settled here. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 24:34 | Yeah, yeah because I believe it’s very important for the people |
| to know what we are doing at the CWS. Um, after, uh, before | ||
| thirty day we make a, like a home visit, next home visits to the | ||
| family to make sure that everything’s OK with them. And then | ||
| the unit this time our colleagues register those kids to the |
school if they required or if their ages are OK with the school. Um, uh, we invite the in the household or like a mother and a father to our office if they have a kid’s over 18. They need to, they need to starting job. So we tried to find a job for these families, on some of them online. Some of them is a, uh, like a face visiting to work with a place and apply for them until they get the job. Then, uh, we just, uh, provide the, if they need in case any other issues, help. Uh, and we also decided that we have a one person, she’s a responsible to, eh, learn them how the transportation to the city, for example, if they need anything, any places they do like a training for him, for the transportation, how they use it. And they provide the ticket. Is pretty good for them, for the beginning to not spending their
| money. It’s like a service now, CWS provided. After that, when | ||
| they passed three months they changed it, they transfer it from | ||
| the RMP to RSS. RSS, if they, you know, they are not much | ||
| involved with a match grant we not providing and not give them | ||
| any other money. Uh, but just we, uh, help them to, if they need | ||
| a job, we’ve helped them. If they need the uh, any health issues | ||
| we can help them. And also about the education, in case they | ||
| need any other extra help, we can help them for this. That’s our | ||
| responsibility. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 26:52 | That’s great! Um, so, so when you came here to the United |
| States, were there any culture shocks when you came here? Or | ||
| was there anything that really surprised you? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 27:03 | Actually, it’s not surprised me a hundred percent because of, |
| you know, I worked with the United States army in our country, | ||
| and, uh, during my job with them as interpreter sometimes we | ||
| would, uh, like a friendly, we speak together. And I learned how | ||
| the people living in the United States how, for example, how | ||
| much they have to pay for rent, how much they have pay to use | ||
| electricity, the internet and all these things. I collect some | ||
| information before we arrived, but. But it’s, you know, it’s not | ||
| like people, eh speaking something and you go into the place | ||
| and see what’s happening there. It’s totally different. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 27:03 | Yeah. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 27:03 | You understand what I mean? |
| Maria Matlock: | 27:03 | Yeah. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 27:55 | It’s a little bit surprised but a too much. But maybe it’s a |
| surprise for, for other people. Who’s not having communicate | ||
| with United States people before going to be like a totally | ||
| different. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 28:20 | Yeah. Have you liked living in Harrisonburg? Have you felt |
| welcomed in this community? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 28:29 | Yes. I like Harrisonburg so much. It’s a very quiet city. The |
| people here is very nice. I like to be on, also is good for like a, | ||
| for the family. It’s a very good area to live and I decided, also | ||
| uh, decide that I’m now starting to process to buy a house for… | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 28:29 | Oh Wow! |
| Arsalan Syan: | 28:51 | myself on my family because you know, decided that we |
| staying here, and we prefer to stay in Harrisonburg, not that | ||
| other places in United States. So we staying. Yeah. We decided | ||
| to stay here. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 29:09 | That’s great! See, so you mentioned that there’s a pretty strong |
| Kurdish community here. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 29:09 | Yes. |
| Maria Matlock: | 29:13 | So, I know that last year there was a referendum about Kurdish |
| independence. How did the community react to that? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 29:13 | I’m not understanding what you mean? |
| Maria Matlock: | 29:23 | Um, so last year there was the referendum on Kurdish |
| independence. How did the Kurdish population, like the Kurdish | ||
| community in this area feel about that? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 29:35 | Uh, actually, uh, it was, uh, uh, we communicate with each |
| other about the independence referendum, it was easy for us to | ||
| apply. It’s a online so we just register and apply online to say yes | ||
| to independent. And we applied. Me, my wife, my sons. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 29:59 | And you all voted for independence? |
| Arsalan Syan: | 29:59 | Yes. I like independence. |
| Maria Matlock: | 30:06 | Um, So what was it like when you found out that, uh, they |
| actually weren’t granted their independence? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 30:13 | Ah, I’m not understanding what you mean? |
| Maria Matlock: | 30:16 | Um, so I believe in the referendum they ended up not getting |
| independence. So how did that feel seeing them not getting | ||
| that? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 30:29 | Well, I feel sad about that. Because, uh, uh, you know, the, the |
| referendum is a, like a first step, the first step that the people | ||
| who’s living in the same places that they are decide to be | ||
| independent with the other parts. It’s like, our right. It’s our | ||
| right to say that’s our dream. But if the political situation in the | ||
| world is against this decision, that’s not our fault. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 30:29 | Yeah. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 31:03 | That’s the work the for that and not accepted the this uh, uh, |
| it’s a democracy process. So we applied a democracy process to | ||
| get the independent with other parts of Iraq, that’s our right. | ||
| And we not say that we are going to eh, use a military for this | ||
| issue. Just we have a vote. So I think totally is democracy for us | ||
| to ask the world to accept that we are a Kurdish people, we | ||
| have a dream to be independent with other part. Especially, you | ||
| have a totally different culture, different language, uh, | ||
| everything we are different, not like other people, so we have a | ||
| right to have a independent, and to have our flag in there, in the | ||
| United Nations. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 31:58 | Um, so do you think that they’ll maybe have another |
| referendum on that? Or do you think independence is still | ||
| something that they can have? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 32:05 | Eh, Kurdistan people make it a referendum and they register, |
| they voted for the firm. So I believe it’s not needed to do that | ||
| another time. Because already it’s available, and registered, and | ||
| all the world know that uh, uh, around eighty or eighty five | ||
| percent of the Kurdistan people, they have a dream to be | ||
| independent. So I believe it’s not necessary to do this process | ||
| again. Even even if, uh, if we do that because you, it’s | ||
| complicated. Because, uh, uh, Kurdistan, the big country of | ||
| Kurdistan, it was a separated after the Second World War. To, | ||
| four places, four countries. So part of us with Iraq, part of us | ||
| was the other part of Syria, and the other Turkey, and the other | ||
| Iran. I believe if we, uh, make another referendum that’s not | ||
| only for our part. Is going to be like a majority for all the Kurdish | ||
| people in the world. In those countries, together. And maybe | ||
| it’s going to be useful also to do, another referendum, but | ||
| including all the parts together. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 33:30 | Yeah, so how has the conflict in Syria affected, uh….like have |
| you gotten any refugees from Syria in recent years? Or what | ||
| kind of, what areas do the refugees you work with come from? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 33:40 | Actually, after I started working there is no refugee coming new |
| um, from uh, Iraq or Syria. Only I received one refugee, who is |
also on a special immigration visa from Afghanistan. The family’s from Afghanistan, uh, they arrived 2017 to December. So only this family I recieved now. But uh we have a newcomer. But during this time there is some family from coming, but they is from Cambodia, from Eritrea, or from other places, not in Middle East.
| Maria Matlock: | 34:20 | Yeah, So do you think that has something to do with President |
| Trump’s travel bans? Or maybe just the growing, um, hostility | ||
| towards refugees from that part of the world in this country? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 34:38 | I believe yes, Mr. Trump effect it. Effective to not the people |
| coming from Iraq or Syria or the Middle East, totally. Uh, maybe | ||
| that’s his decision effected negative on people, and it’s not | ||
| going to be easy for people who’s a already applied to come to | ||
| United State. And they have a right, because the law of the | ||
| United States that allow him to, to come to United State | ||
| because, uh, they have, uh, cases, um, it’s approved already. | ||
| And there’s many, many cases approved from the Special, eh, | ||
| special agencies that are responsible for that. But uh, maybe I | ||
| believe it’s a Mr. Trump’s, eh Trump’s decision that these | ||
| people is not coming anymore, and that’s affecting negatively. | ||
| Maybe. Because some people need really to come here to the | ||
| United States. They are not safe in these countries. Yeah. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 35:50 | Well, I believe that’s all the questions that I have. Um, let’s see. |
| Is there anything that you would like to talk about? Like maybe | ||
| your experiences either in Iraq or here in the US? | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 36:03 | We’ll, uh, for the people that I believe when they arrived to the |
| United States there is two challenge. The first one is the | ||
| language and the second one is the health…health insurance. | ||
| That’s, two things is like a challenge for everybody. If he came | ||
| from any other country he have to face-to-face with these two | ||
| challenge. Especially the language, if you… the key to, to the | ||
| language is the key to, to, to be a part of this, uh, country. To | ||
| understand, to communicate with people. So I prefer, and I | ||
| suggest is also to CWS, to make focus on this issue for the | ||
| people, especially when they come to the United States in the | ||
| beginning and they have no language. They have no skill to | ||
| speak English. So, uh, but it’s not easy to find, like a special | ||
| places to learn English. There is some places like a Skyline, like | ||
| other businesses in the JMU, you also. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 37:37 | Last year it was some classes, but this is not available. I’m not |
| happy with that. Last year there was a semesters for the people | ||
| who’s coming. They just pay $25 per semester. It’s was, uh I was | ||
| very happy with that service available at JMU, but I don’t know | ||
| why this year they decided to not the provide the services to | ||
| the refugee. Uh, from there I asked him again…ask the JMU to | ||
| open this service to the refugee because it’s really important. | ||
| Excuse me… | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 37:37 | Oh, it’s fine! |
| Arsalan Syan: | 37:37 | [Speaking to his son, Ali, in Arabic] |
| Arsalan Syan: | 38:09 | And also, uh, uh, as I mentioned, uh, the language and the |
| health insurance. The health insurance is in the United States, | ||
| the process is, I believe it’s very complicated for a newcomer. In | ||
| the beginning, a social service provide the Medicaid during the | ||
| six or one year to the newcomer family. But after that they not | ||
| provide these services. And the people have to find a, uh, | ||
| insurance by themselves or during [their] job. And during the | ||
| job, you have to spend monthly or weekly, you have to pay for | ||
| that and it’s going to be like a extra load to the new family. I | ||
| believe if the social services or United State health department | ||
| make a decision or help his people for at least three years, at | ||
| least three years, they provide medical insurance to those | ||
| families who’s coming new. And then after that, maybe they | ||
| learn better. For me, for me myself, uh, I speak English good, | ||
| and I have a graduate university, and I maybe have a mind for | ||
| how to arrange these things for me and my family. But there’s | ||
| people coming, they cannot, believe me, They need to learn | ||
| how they opened the door. They need like a lecture to open the | ||
| door or how to use the…excuse me… how to use the showers. | ||
| They coming from Africa and they have no experience for | ||
| nothing if they live in the open area before they come. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 40:01 | So these people need at least three years health insurance to |
| be, to be a learning. Uh, after that they did this three years, It’s | ||
| helped them to learn English and they find a job. And doing the | ||
| job, they learn how they communicate with people and what is | ||
| the required to the family. Like a health insurance, like a | ||
| transportation. There’s people who come to here, and maybe | ||
| they not use the card. So these kind of people is not easy for | ||
| them. Maybe for me it’s easy to, to, to involved with the new | ||
| country, like the United States, or any other country. But for | ||
| other people it’s not easy. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 40:01 | Yeah, I’m sure it’s very difficult. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 40:52 | Yes, very difficult. That’s why I maybe many, many of the |
| refugees, they are not happy. Because these two things. First | ||
| the language assistant and the second thing the health | ||
| insurance. That’s my opinion. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 41:04 | I’m sure it’s difficult. I can’t even imagine, you know, picking up |
| and moving to a completely new area like that. Um… | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 41:04 | You find any question? |
| Maria Matlock: | 41:16 | Um, I think that’s, that’s everything. Thank you for talking to us. |
| This is very interesting. Is really awesome. Getting to hear your | ||
| story. | ||
| Arsalan Syan: | 41:22 | Thank you so much for you. Throw a house and the discuss this |
| position together. Hopefully it’s going to be like a a voice to to | ||
| tell somebody in the United State that these things is happening | ||
| and this is required. Especialty for that new refugees and I thank | ||
| you again for coming. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 41:22 | Yes, thank you so much. |
| Arsalan Syan: | 41:22 | Have a great day and hopefully you pass this project! I am |
| happy you are here. | ||
| Maria Matlock: | 41:22 | Thank you so much. |
 Loading...
Loading...